Although vitamin C (ascorbic acid) is one of the most popular vitamin supplements in the US, it is also one of the most controversial. Vitamin C works as an antioxidant in aqueous environments of the body both inside and outside cells. Most other animals can manufacture their own vitamin C, but humans do not have that luxury. Over many years of research, respected scientists have shared varying views on the importance of vitamin C quantities we need in our daily diets, but what is clear is that has an essential role in human health.
The main function of vitamin C is the production of collagen, the main protein substance of the human body. It aids the joining of a portion of a molecule of the amino acid proline to form hydroxyproline, resulting in a stable collagen structure, and therefore the proteins hold together connective tissues. Vitamin C is vital for wound repair, healthy gums, and the prevention of easy bruising.
Another beneficial affect of vitamin C is on the immune system. Vitamin C also critically affects various immune functions by enhancing white blood cell function and activity, and increasing interferon levels, carnitine synthesis, antibody responses, and secretion of thymic hormones.
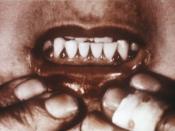
The main negative affect of vitamin C deficiency is a disease called scurvy. The most common symptoms of scurvy are bleeding gums, poor wound healing, and extensive bruising. Further infection developing from scurvy includes infection hysteria and mild depression. The rare negative affects to having too much vitamin C most common are diarrhea, intestinal distension, gas, or more severely, calcium oxalate kidney stones.
Although vitamin C can be found in many citrus fruits, it is most plentiful in vegetables such as broccoli, peppers, potatoes, and brussel sprouts. Exposure to air often destroys vitamin C; so eating fresh foods becomes...